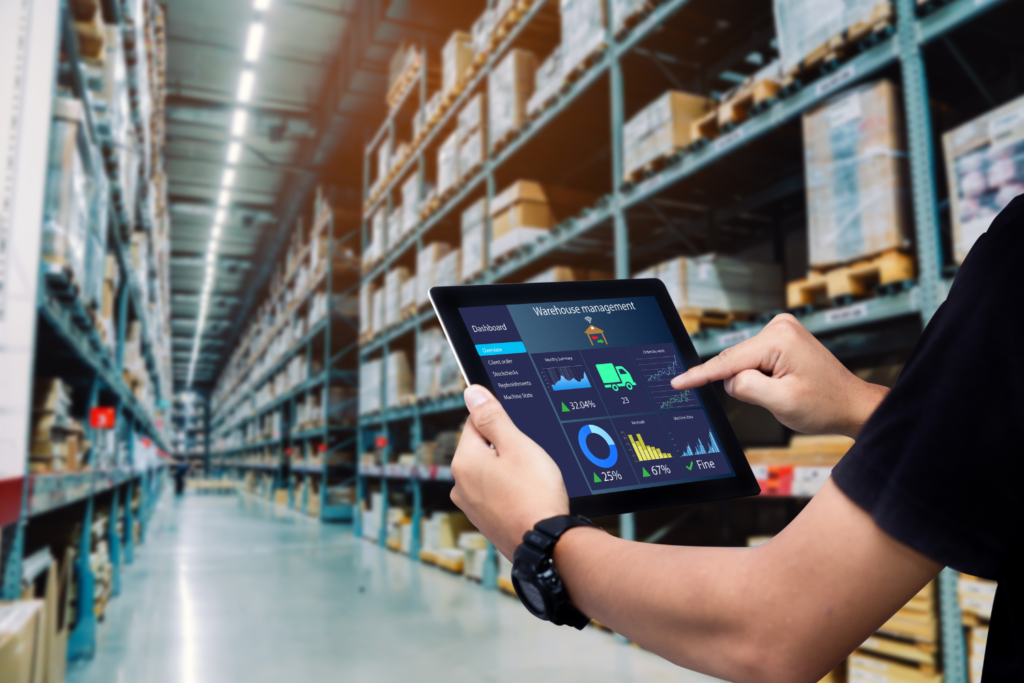
Warehouse automation refers to the use of technology, machinery, and software to perform tasks within a warehouse with minimal or no human intervention.
It can range from basic systems like conveyor belts to advanced technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and fully integrated warehouse management systems.
Let us discuss warehouse automation, its benefits, and the most common systems below.
What Is Warehouse Automation?
Warehouse automation uses technology and software to streamline tasks like inventory management, order picking, and material handling with minimal human input.
It increases efficiency, reduces costs, and improves accuracy by automating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and speeding up operations.
It also ensures safer workplaces by handling dangerous or physically demanding jobs and optimizes storage space through better layouts.
Supply chains have become increasingly complex and customer expectations continue to rise. You can stay competitive if you automate your processes.

8 Benefits of Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation enables you to handle larger volumes and meet demands without spending more money and hiring more workers.
You can learn more about its benefits below.
1. It Automates Repetitive Tasks and Speeds Up Processes
Warehouse automation excels at handling tasks that are monotonous and time-intensive, such as picking, packing, sorting, and inventory management.
These tasks, when performed manually, often slow down operations due to human limitations like fatigue or the need for frequent breaks.
2. It Reduces the Risk of Workplace Injuries by Automating Dangerous Tasks
Warehouses are often environments where physical labor involves inherent risks.
Tasks such as heavy lifting, working at heights, or operating machinery can result in injuries if not executed properly.
Warehouse automation minimizes such risks by delegating hazardous activities to machines specifically designed for these purposes.
3. It Reduces Human Errors
Automated systems rely on programmed precision and data consistency, so they reduce errors.
Human error is a common issue in warehouses, particularly during repetitive tasks or under high-pressure conditions.
It can lead to costly consequences, such as incorrect shipments, stock discrepancies, or dissatisfied customers.
4. It Lowers Labor Costs and Increases Productivity
With machines handling repetitive and time-consuming tasks, fewer employees are needed to achieve the same, if not higher, levels of productivity.
You can allocate human resources to more strategic and value-adding roles, such as quality control or customer service.
5. It Can Handle Increased Volumes During Peak Times
Seasonal peaks, such as holiday shopping periods or promotional events, often result in increased order volumes that can overwhelm traditional warehouse systems.
Automated warehouses are inherently scalable and flexible, allowing you to handle such surges efficiently.
Robots and automated systems can be programmed to ramp up their activity levels without requiring additional training or onboarding, unlike human employees.
Temporary adjustments, such as increasing conveyor belt speeds or deploying extra AMRs, can also be implemented seamlessly.
6. It Optimizes Storage Space and Improves Warehouse Layout
Automated systems like AS/RS and robotic shelving units maximize the use of warehouse height, reducing the need for horizontal expansion.
These systems also simplify retrieval by precisely locating and delivering items without requiring human navigation through narrow aisles.

7. It Provides Real-Time Inventory Tracking and Data Analytics
Automated systems integrate advanced tracking and data management tools that provide real-time visibility into inventory levels and locations.
Technologies like RFID tags and IoT-enabled devices continuously update inventory data as goods move through the warehouse.
8. It Reduces Energy Consumption and Promotes Sustainable Practices
Modern automated systems are designed with energy efficiency in mind, incorporating features like low-power consumption modes and energy recovery mechanisms.
For instance, conveyor systems can be equipped with sensors that activate only when items are present, conserving electricity during idle times.
Automated lighting systems and smart HVAC controls further contribute to energy savings by adjusting to real-time warehouse activity.
Faster and more accurate order processing also reduces the need for excess packaging, so it helps you reduce waste and be more sustainable.
10 Most Common Warehouse Automation Systems
Below are the most common warehouse automation systems used by businesses across the world.
1. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) consist of cranes, shuttles, or carousels that navigate storage areas to place or retrieve items.
They operate through software integration that precisely identifies the location of goods.
2. Conveyor Systems
Conveyor systems facilitate the smooth movement of items along fixed pathways, reducing the manual effort involved in transporting goods across different sections of the facility.
They come in various types, such as roller, belt, and pneumatic systems, and can be integrated with sensors and control systems to automate sorting and routing.
3. Goods-to-Person (G2P) Systems
Goods-to-Person (G2P) systems use automated storage units or robots to retrieve items and deliver them to designated workstations.
They reduce the time and effort involved in order fulfillment, as workers interact with items at ergonomic stations where picking is streamlined.
4. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) navigate warehouse floors independently, using sensors, cameras, and mapping software to avoid obstacles and determine optimal routes.
Unlike traditional conveyor systems, they adapt to dynamic warehouse layouts, making them suitable for facilities with frequently changing storage configurations.
They transport goods, assist in picking processes, and replenish inventory.
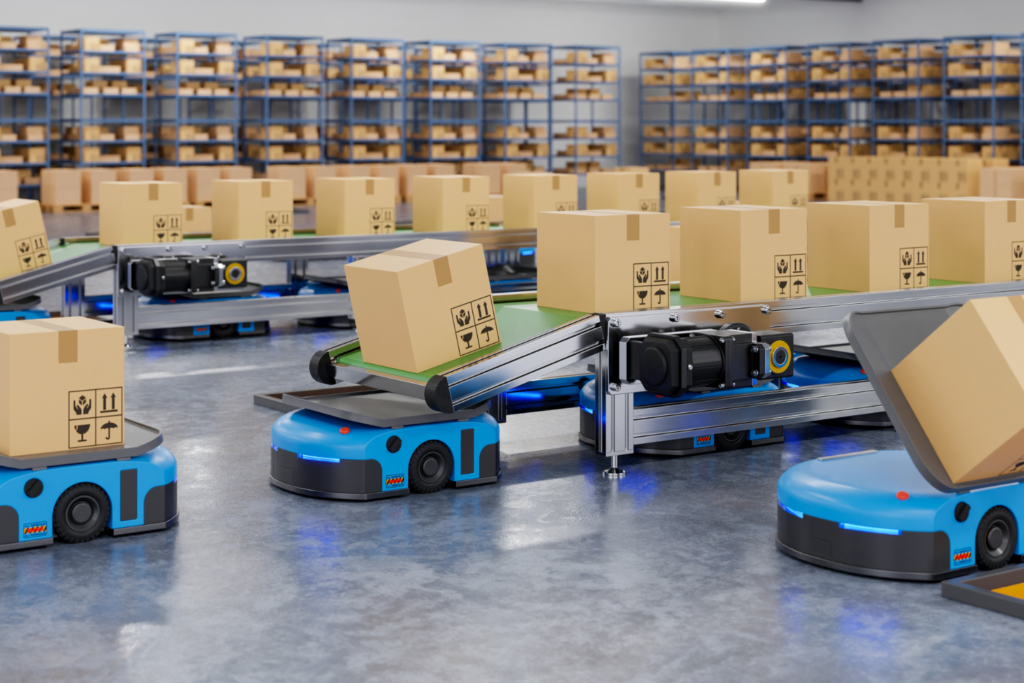

5. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are similar to AMRs but rely on fixed paths, such as magnetic strips or marked lines, to navigate warehouse floors.
They are ideal for transporting heavy loads, pallets, or bulk materials over long distances within a facility.
6. Pick-to-Light Systems
Pick-to-light systems use light indicators on storage locations to guide workers to the correct items for an order.
Once the item is picked, the worker confirms the action, and the system updates inventory records in real time.
This method significantly reduces errors and speeds up the picking process, as workers do not need to rely on printed lists or handheld devices.
7. Put-to-Light Systems
Put-to-light systems use illuminated indicators at designated bins or areas to direct workers on where to place items for specific orders.
This is essential for batch-picking operations, where multiple orders are processed simultaneously.
8. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is the digital brain of warehouse automation, orchestrating all aspects of inventory management and operations.
It tracks inventory in real time and integrates seamlessly with other automation technologies, such as AS/RS, AMRs, and conveyor systems, to ensure cohesive operations.
9. Robotic Systems
Robotic systems encompass a broad range of technologies that automate various warehouse tasks.
From robotic arms that handle precise picking and packing to collaborative robots (cobots) that assist workers in repetitive tasks, these systems are transforming the way warehouses operate.
Their ability to work continuously without fatigue makes them ideal for high-demand environments.
10. Scanning Hardware
Devices such as barcode scanners, RFID readers, and handheld terminals capture and record data about items as they move through the warehouse.
These tools integrate with warehouse management systems to provide real-time updates on inventory status, location, and movement.

Conclusion
Warehouse automation helps you adjust to fluctuating volumes without the need to hire additional staff.
You can increase throughput without compromising accuracy or efficiency, ensuring that you can handle the demand without falling short on service levels.
If you need logistics assistance, check out our services here.
Chesapeake Pallets has been helping companies across the United States level up their logistics, one pallet at a time.
For inquiries, email info@chesapeakepallets.com or request a quote below!